| Citation: | SUN Meiling, ZHAO Fanghua, GAO Man, ZHEN Siyuan, CHEN Yueling, Ramon Maria Calduch, LI Haiyan. Hotspots and comparative analysis of international acupuncture research over the past decade via Web of Science[J]. Digital Chinese Medicine, 2023, 6(1): 28-40. DOI: 10.1016/j.dcmed.2023.02.002 |
Acupuncture is an ancient Chinese treatment that has been systematically used for over 3 000 years [1]. In the past decade, acupuncture has received wide attention in Asia, North America, Europe, Oceania, and other countries and regions. Acupuncture research has also developed rapidly during this period, and the relevant articles published reflect its evolution process [2, 3].
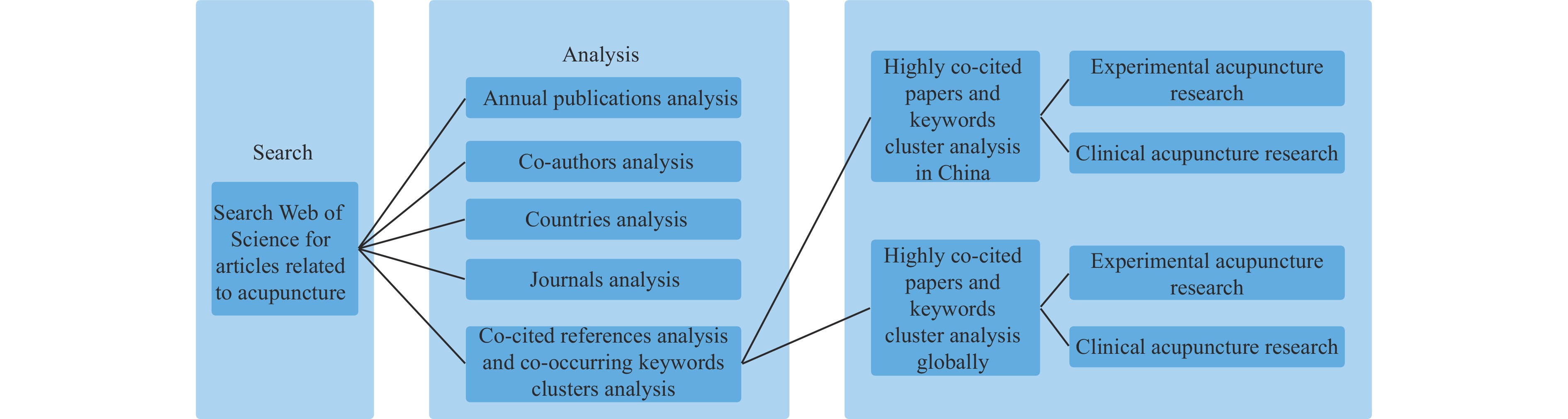
In order to comprehensively understand the application of acupuncture in China and abroad, the relevant research on acupuncture in China and abroad was sorted out and compared to summarize and predict the application status and development trend of acupuncture. This study mainly adopts the CiteSpace 6.1.R3 visualization tool to systematically study the published information of acupuncture literature retrieved from the Web of Science database in recent 10 years, in order to reveal the current status and trends of international acupuncture research.
This study used the Web of Science database as the data source, with specific search formulas as shown below set for the time span from January 1, 2012 to December 31, 2021. The “CU” is a specific field tag in the Web of Science advanced search. Papers with Chinese and non-Chinese authors collaborating were included in China's scope due to searching formula restrictions.
The search strategy for experimental research on acupuncture in China is as follows: TS = [“acupuncture” AND (“rat” OR “rats” OR “dog” OR “dogs” OR “mice” OR “horse” OR “veterinarian” OR “veterinary” OR “animal” OR “mouse model” OR “rabbit” OR “cat”) NOT (“human” OR “clinical trial” OR “meta-analysis”)] AND CU = (“China”).
The search strategy for clinical research on acupuncture in China is as follows: TS = [“acupuncture” AND(“clinical trial” OR “clinical-trial” OR “case reports” OR “randomized clinical-trial” OR “randomized controlled trial” OR “randomized clinical trial” OR “randomized study” OR “in patient” OR “women” OR “randomized, parallel” OR “randomized trial” OR “a comparative clinical pilot study” OR “a prospective observational study” OR “meta-analysis” OR “meta analysis” OR “children” OR “a randomized crossover” OR “investigation” OR “double-blind” OR “double blind” OR “single-blind” OR “a pilot study” OR “elderly person” OR “systematic review” OR “prospective survey” OR “a feasibility study” OR “volunteers” OR “treat” OR “efficacy” OR “controlled trial” OR “trial” or “clinical trials” OR “Cochrane review” OR “cohort of” OR “healthy human” OR “healthy subjects” OR “people”)] AND CU = (“China”).
The search strategy for experimental research on acupuncture abroad is as follows: TS = [“acupuncture” AND (“rat” OR “rats” OR “dog” OR “dogs” OR “mice” OR “horse” OR “veterinarian” OR “veterinary” OR “animal” OR “mouse model” OR “rabbit” OR “cat”) NOT (“human” OR “clinical trial” OR “meta-analysis”)] NOT CU= (“China”).
The search strategy for clinical research on acupuncture abroad is as follows. TS = [“acupuncture” AND (“clinical trial” OR “clinical-trial” OR “case reports” OR “randomized clinical-trial” OR “randomized controlled trial” OR “randomized clinical trial” OR “randomized study” OR “in patient” OR “women” OR “randomized, parallel” OR “randomized trial” OR “a comparative clinical pilot study” OR “a prospective observational study” OR “meta-analysis” OR “meta analysis” OR “children” OR “a randomized crossover” OR “investigation” OR “double-blind” OR “double blind” OR “single-blind” OR “a pilot study” OR “elderly person” OR “systematic review” OR “prospective survey” OR “a feasibility study” OR “volunteers” OR “treat” OR “efficacy” OR “controlled trial” OR “trial” or “clinical trials” OR “Cochrane review” OR “cohort of” OR “healthy human” OR “healthy subjects” OR “people”)] AND CU = (“China”).
(i) Articles on acupuncture research obtained through retrieval on the Web of Science.
(ii) Types of articles: original research articles, reviews, conference proceedings, and online articles.
(iii) Time of publication: January 1, 2012 to December 31, 2021.
(iv) Language: English.
(i) Articles that required manual searching.
(ii) Corrected papers and book chapters.
(iii) Duplicate articles.
(iv) Articles unrelated to acupuncture research.
First, the name of each institution was unified as the first-level name of the institution. For example, “School of Acupuncture-Moxibustion and Tuina, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine” was standardized as “Beijing University of Chinese Medicine”. Second, the name of the country was unified into the official name. For example, “PEOPLES R CHINA” was standardized as “China”. Finally, the included literature in the RefWorks format in the Web of Science was exported and imported into CiteSpace 6.1.R3 software for format conversion after being renamed “download_.txt”.
CiteSpace 6.1.R3 is a multivariate, time-sharing, and dynamic knowledge-mapping tool [4]. For the software parameter settings, the time span was set from January 1, 2012 to December 31, 2021, and the time partition was one year as a unit under the “Time Slicing” module. In the formed knowledge map, different nodes represent different authors or countries, and the size of nodes or fonts reflects their productivity. The connection strength between nodes indicates the cooperation strength between countries and authors. Additionally, the CiteSpace algorithm is used to cluster keywords into different groups. Each cluster is identified with a different color. The label size of the term indicates the number of acupuncture articles of the term. The articles were stratified and systematically analyzed according to the year of articles, authors, countries, and journals. Furthermore, the references and keywords of articles in China and abroad were assessed and analyzed from clinical and experimental medicine aspects. The research process of this paper is shown in Figure 1.
Through searching and screening, there are a total of 1 215 articles in the field of acupuncture experimental medicine, and 3 805 articles in the field of acupuncture clinical medicine in China; 551 articles in the field of acupuncture experimental medicine, and 4 538 articles in the field of in acupuncture clinical medicine abroad. These four parts of the literature have duplicate records, and a total of 9 155 articles were obtained after duplication by CiteSpace software. The data process is shown in Figure 2.
The annual changes in the number of articles issued in the field of acupuncture in China and abroad in recent 10 years are shown in Figure 3. It can be seen that the trend of the number of foreign annual articles is stable and flat, with a small fluctuation and an average of 475 articles per year. The number of annual articles in China has shown a trend of gradual growth, with the largest increase in 2020 (an increase of 205 articles compared with the previous year) and an average annual release of 440 articles. By comparison, the cumulative amount of foreign acupuncture research articles has been greater than that of domestic research in the past decade. From 2012 to 2018, the number of foreign acupuncture research articles was higher than that of domestic research articles, and the number gap generally decreased annually. After 2018, the number of domestic acupuncture articles was higher than that of foreign research articles, and the number gap had been increasing annually.
| No. | Author | Institution | Country | n (%) |
| 1 | LIU Cunzhi | Beijing Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine | China | 90 (0.98%) |
| 2 | Lee Myeong Soo | Korea Institute of Oriental Medicine | South Korea | 89 (0.97%) |
| 3 | LIU Zhishun | China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences | China | 80 (0.87%) |
| 4 | LAO Lixing | University of Hong Kong | China | 75 (0.82%) |
| 5 | LIANG Fanrong | Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine | China | 68 (0.74%) |
| 6 | Park Hi Joon | Kyung Hee University | South Korea | 61 (0.67%) |
| 7 | LI Ying | Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine | China | 59 (0.64%) |
| 8 | YANG Jingwen | Hefei University of Technology | China | 57 (0.62%) |
| 9 | SHI Guangxia | Beijing University of Chinese Medicine | China | 50 (0.55%) |
| 10 | ZHAO Ling | Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine | China | 49 (0.54%) |
The cooperation of authors in the field of acupuncture research is shown in Figure 4. We imported the research literature into CiteSpace 6.1.R3 software, then selected “author” for the node and the top n was set to 20, selected “pruning the merged network” for the pruning algorithm, and finally drew the knowledge map. It can be seen that in the knowledge map, network structure of four author collaboration group are mainly formed, namely, the network structure centered on Kim Tae-hun from Kyung Hee University, with the research focusing on the acupuncture treatment scheme of chronic kidney disease and the systematic review of acupuncture clinical research [5, 6]; the network structure centered on Lee Myeong Soo from Korea Institute of Oriental Medicine and Park Hi Joon from Kyung Hee University, with the research focusing on systematic summary of acupuncture treatment of gynecological diseases and low back pain [7, 8]; the network structure centered on LIANG Fanrong and LI Ying from Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, with research focusing on the experimental study of acupuncture and treatment of primary dysmenorrhea and migraine [9, 10]; the network structure centered on LIU Cunzhi from Beijing Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine affiliated to Capital Medical University and WANG Liqiong from Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, with the research focusing on the effect of acupuncture and related symptoms after stroke [11].
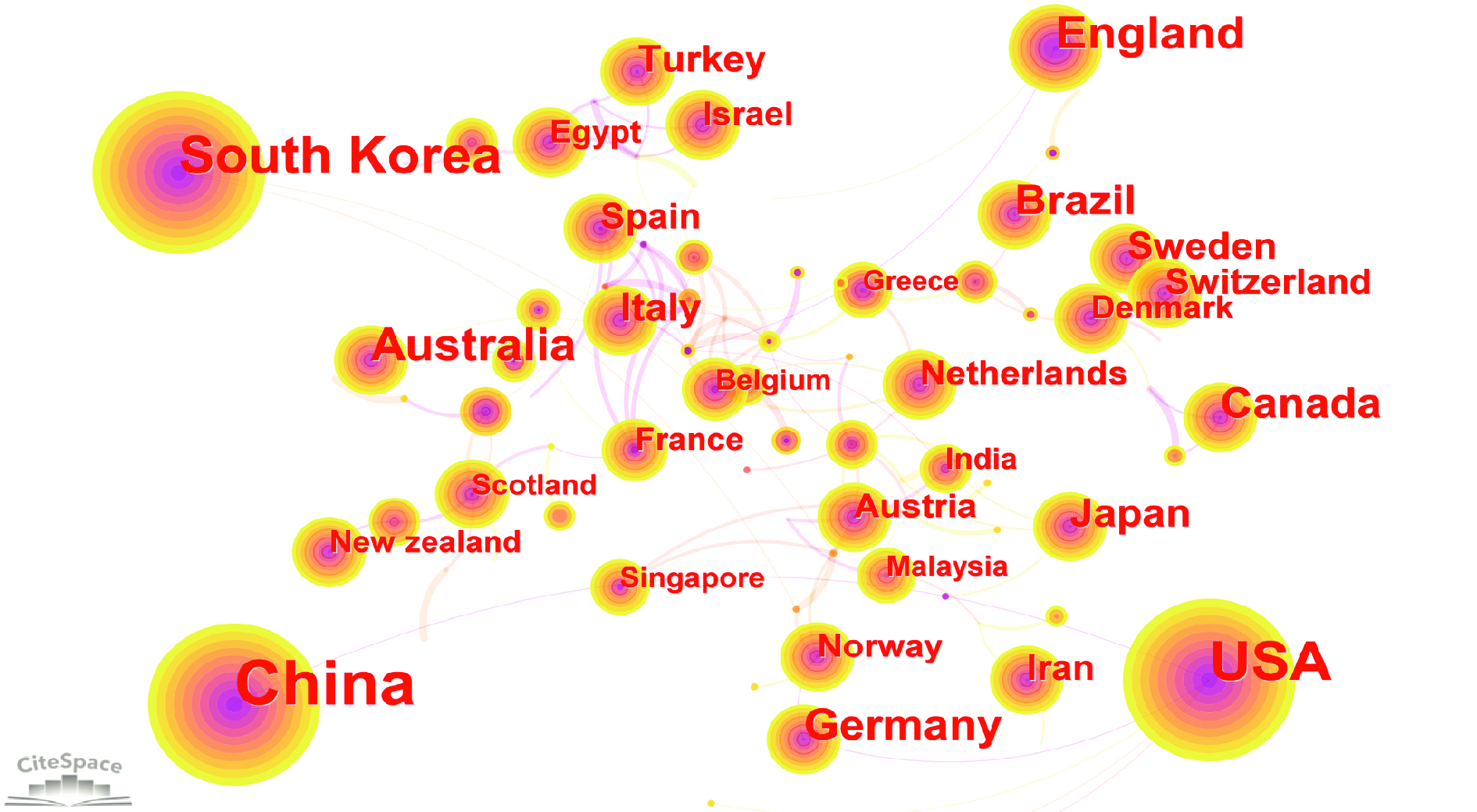
From 2012 to 2021, 95 countries and regions participated in acupuncture research, with the high contributing countries and regions shown in Table 2 and Figure 5. China had the highest number of articles (4 844, 52.91%), followed by the USA (1 710, 18.68%) and South Korea (964, 10.53%). England contributed 472 articles, accounting for 5.16%, while other countries accounted for less than 5%. However, countries with a high volume of articles do not have many collaborative links, and those with fewer articles have closer collaborative links.
| No. | Country | n (%) |
| 1 | China | 4 844 (52.91%) |
| 2 | USA | 1 710 (18.68%) |
| 3 | South Korea | 964 (10.53%) |
| 4 | England | 472 (5.16%) |
| 5 | Australia | 417 (4.55%) |
| 6 | Germany | 313 (3.42%) |
| 7 | Brazil | 269 (2.94%) |
| 8 | Canada | 256 (2.80%) |
| 9 | Japan | 178 (1.94%) |
| 10 | Italy | 161 (1.76%) |
The top 10 journals following the number of published acupuncture papers are shown in Table 3. The Journal Evidence-based Complementary and Alternative Medicine published the highest number of papers (958, 10.46%), followed by Medical (674, 7.36%) and Acupuncture in Medicine (498, 5.44%), with the other journals publishing under 300 papers. The journal with the largest impact factor was BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine with an impact factor of 4.782, in the JCR Q1 region, followed by PLoS One (3.752, JCR Q2) and Complementary Therapies in Medicine (3.335, JCR Q2). Among the top 10 journals publishing articles in acupuncture research, four are English journals, four American journals, one German journal, and one Chinese journal.
| No. | Journal | IF-2021/JCR | Country | n |
| 1 | Evidence-based Complementary and Alternative Medicine | 2.650/Q3 | England | 958 |
| 2 | Medicine | 1.817/Q3 | US | 674 |
| 3 | Acupuncture in Medicine | 1.976/Q3 | UK | 498 |
| 4 | Trials | 2.728/Q4 | US | 284 |
| 5 | Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine | 2.381/Q3 | US | 256 |
| 6 | BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine | 4.782/Q1 | UK | 224 |
| 7 | European Journal of Integrative Medicine | 1.813/Q4 | Germany | 169 |
| 8 | Complementary Therapies in Medicine | 3.335/Q2 | UK | 166 |
| 9 | Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine | 2.547/Q3 | China | 166 |
| 10 | PLoS One | 3.752/Q2 | US | 160 |
Highly cited papers provide important information about the current state of research in a field, and help to analyze hotspots and trends in the research field [12]. This research produced tables of the top 10 most frequently cited references in literature.
The top 10 highly cited papers on experimental acupuncture research in China are shown in Table 4. The most frequently cited paper is a comparative study in the journal Trends in Neurosciences, which investigated the effects of acupuncture and specific frequencies of electrical stimulation on specific neuropeptides in the central nervous system [13]. The paper with the highest impact factor (51.598, Q1) is a historical article on acupuncture in Annals of Internal Medicine, which provided a general discussion of the historical origins, theoretical doctrines, and therapeutic effects of acupuncture [14]. Other studies focused on model experiments, and mechanistic research of acupuncture analgesia, and electroacupuncture stimulation of nerve receptors.
| No. | Title | Journal | IF-2021/JCR | Total cites | Year |
| 1 | Acupuncture: neuropeptide release produced by electrical stimulation of different frequencies | Trends in Neurosciences | 16.978/Q1 | 79 | 2003 |
| 2 | Adenosine A1 receptors mediate local anti-nociceptive effects of acupuncture | Nature Neuroscience | 28.771/Q1 | 70 | 2010 |
| 3 | Acupuncture and endorphins | Neuroscience Letters | 3.197/Q3 | 34 | 2004 |
| 4 | Quantitative assessment of tactile allodynia in the rat paw | Journal of Neuroscience Methods | 2.987/Q3 | 32 | 1994 |
| 5 | Acupuncture: theory, efficacy, and practice | Annals of Internal Medicine | 51.598/Q1 | 28 | 2002 |
| 6 | A new model of chronic visceral hypersensitivity in adult rats induced by colon irritation during postnatal development | Gastroenterology | 33.883/Q1 | 26 | 2000 |
| 7 | A peripheral mononeuropathy in rat that produces disorders of pain sensation like those seen in man | Pain | 7.926/Q1 | 25 | 1988 |
| 8 | Acupuncture analgesia: areas of consensus and controversy | Pain | 7.926/Q1 | 24 | 2011 |
| 9 | Acupuncture: a novel hypothesis for the involvement of purinergic signalling | Medical Hypotheses | 4.411/Q2 | 22 | 2009 |
| 10 | Electroacupuncture exerts anti-inflammatory effects in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injured rats via suppression of the TLR4/NF-κB pathway | International Journal of Molecular Medicine | 5.314/Q2 | 21 | 2013 |
The top 10 highly cited papers on clinical acupuncture research in China in the last decade are shown in Table 5. The most frequently cited paper with the highest journal impact factor was the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) statement published in the journal BMJ [15]. Papers published in the BMJ were the study of the development of Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development and Evaluation (GRADE) ratings for guideline development [16] and of the measurement of inconsistency in meta-analysis [17]. All the 10 papers were published in the JCR Q1 journals, and are seminal papers in the field of evidence-based and mechanistic research in acupuncture.
| No. | Title | Journal | IF-2021/JCR | Total cites | Year |
| 1 | Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015 statement | BMJ | 93.333/Q1 | 145 | 2009 |
| 2 | Cognitive-behavioural interventions for children who have been sexually abused (Review) | Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews | 12.008/Q1 | 116 | 2012 |
| 3 | Acupuncture: neuropeptide release produced by electrical stimulation of different frequencies | Trends in Neurosciences | 16.978/Q1 | 115 | 2003 |
| 4 | Acupuncture: theory, efficacy, and practice | Annals of Internal Medicine | 51.598/Q1 | 110 | 2002 |
| 5 | Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement | BMJ | 93.333/Q1 | 109 | 2009 |
| 6 | Neural mechanism underlying acupuncture analgesia | Progress in Neurobiology | 10.885/Q1 | 109 | 2008 |
| 7 | GRADE: an emerging consensus on rating quality of evidence and strength of recommendations | BMJ | 93.333/Q1 | 106 | 2008 |
| 8 | Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses | BMJ | 93.333/Q1 | 104 | 2003 |
| 9 | Acupuncture for chronic pain individual patient data meta-analysis | JAMA Internal Medicine | 44.409/Q1 | 104 | 2012 |
| 10 | Revised standards for reporting interventions in clinical trials of acupuncture (STRICTA): extending the CONSORT statement | PLoS Medicine | 11.613/Q1 | 103 | 2010 |
The top 10 highly cited papers on experimental acupuncture research abroad in the last decade are shown in Table 6. The most frequently cited and highest journal impact factor was the research on the mechanism of action of adenosine release during acupuncture stimulation published in the journal Nature Neuroscience [18]. Nine of the papers in the table were published in the JCR Q1 journals, and one in the JCR Q3 journal (Neuroscience Letters), which provided a systematic review of the mechanisms of endogenous opioid peptides such as endorphins in mediating electroacupuncture analgesia [19].
| No. | Title | Journal | IF-2021/JCR | Total cites | Year |
| 1 | Adenosine A1 receptors mediate local anti-nociceptive effects of acupuncture | Nature Neuroscience | 28.771/Q1 | 63 | 2010 |
| 2 | Neural mechanism underlying acupuncture analgesia | Progress in Neurobiology | 10.885/Q1 | 56 | 2008 |
| 3 | Acupuncture: neuropeptide release produced by electrical stimulation of different frequencies | Trends in Neurosciences | 16.978/Q1 | 48 | 2003 |
| 4 | A proposed transpositional acupoint system in a mouse and rat model | Research in Veterinary Science | 2.554/Q1 | 48 | 2008 |
| 5 | Ethical Guidelines for investigations of Experimental Pain in Conscious Animals | Pain | 7.926/Q1 | 30 | 1983 |
| 6 | Acupuncture and endorphins | Neuroscience Letters | 3.197/Q3 | 28 | 2004 |
| 7 | Mechanisms of acupuncture-electroacupuncture on persistent pain | Anesthesiology | 8.986/Q1 | 27 | 2014 |
| 8 | Mechanical signaling through connective tissue: a mechanism for the therapeutic effect of acupuncture | Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology Journal | 5.834/Q1 | 23 | 2001 |
| 9 | Therapeutic application of anti-arthritis, pain-releasing, and anti-cancer effects of bee venom and its constituent compounds | Pharmacol Therapeut | 13.400/Q1 | 23 | 2007 |
| 10 | The central serotonergic system mediates the analgesic effect of electroacupuncture on Zusanli (ST36) acupoints | Journal of Biomedical Science | 12.771/Q1 | 22 | 2004 |
The top 10 highly cited papers on clinical acupuncture research abroad in the last decade are shown in Table 7. The most frequently cited was a meta-analysis of studies of acupuncture for chronic pain published in the Archives of Internal Medicine [20], and the journal with the highest impact factor was a survey study of trends in the use of alternative medicine in the USA published in 1998 [21]. Other acupuncture studies have focused on survey analyses and retrospective studies of patients’ data.
| No. | Title | Journal | IF-2021/JCR | Total cites | Year |
| 1 | Acupuncture for chronic pain individual patient data meta-analysis | Archives of Internal Medicine | 44.409/Q1 | 254 | 2012 |
| 2 | Neural mechanism underlying acupuncture analgesia | Progress in Neurobiology | 10.885/Q1 | 157 | 2008 |
| 3 | Acupuncture and endorphins | Neuroscience Letters | 3.197/Q3 | 112 | 2004 |
| 4 | German acupuncture trials (GERAC) for chronic low back pain | Archives of Internal Medicine | 44.409/Q1 | 106 | 2007 |
| 5 | Introducing a placebo needle into acupuncture research | The Lancet | 202.731/Q1 | 104 | 1998 |
| 6 | Safety of acupuncture: results of a prospective observational study with 229 230 patients and introduction of a medical information and consent form | Forschende Komplementarmedizin | 1.306/Q4 | 98 | 2009 |
| 7 | Acupuncture: theory, efficacy, and practice | Annals of Internal Medicine | 51.598/Q1 | 94 | 2002 |
| 8 | Trends in alternative medicine use in the United States, 1990 -1997 results of a follow-up national survey | JAMA | 157.335/Q1 | 93 | 1998 |
| 9 | The impact of patient expectations on outcomes in four randomized controlled trials of acupuncture in patients with chronic pain | Pain | 7.926/Q1 | 93 | 2007 |
| 10 | Adenosine A1 receptors mediate local anti-nociceptive effects of acupuncture | Nature Neuroscience | 28.771/Q1 | 91 | 2010 |
Keywords act as high generalization of the content of the literature, which reveals the research focus and contributes to the understanding and analysis of the theme and research content of the whole literature [22].
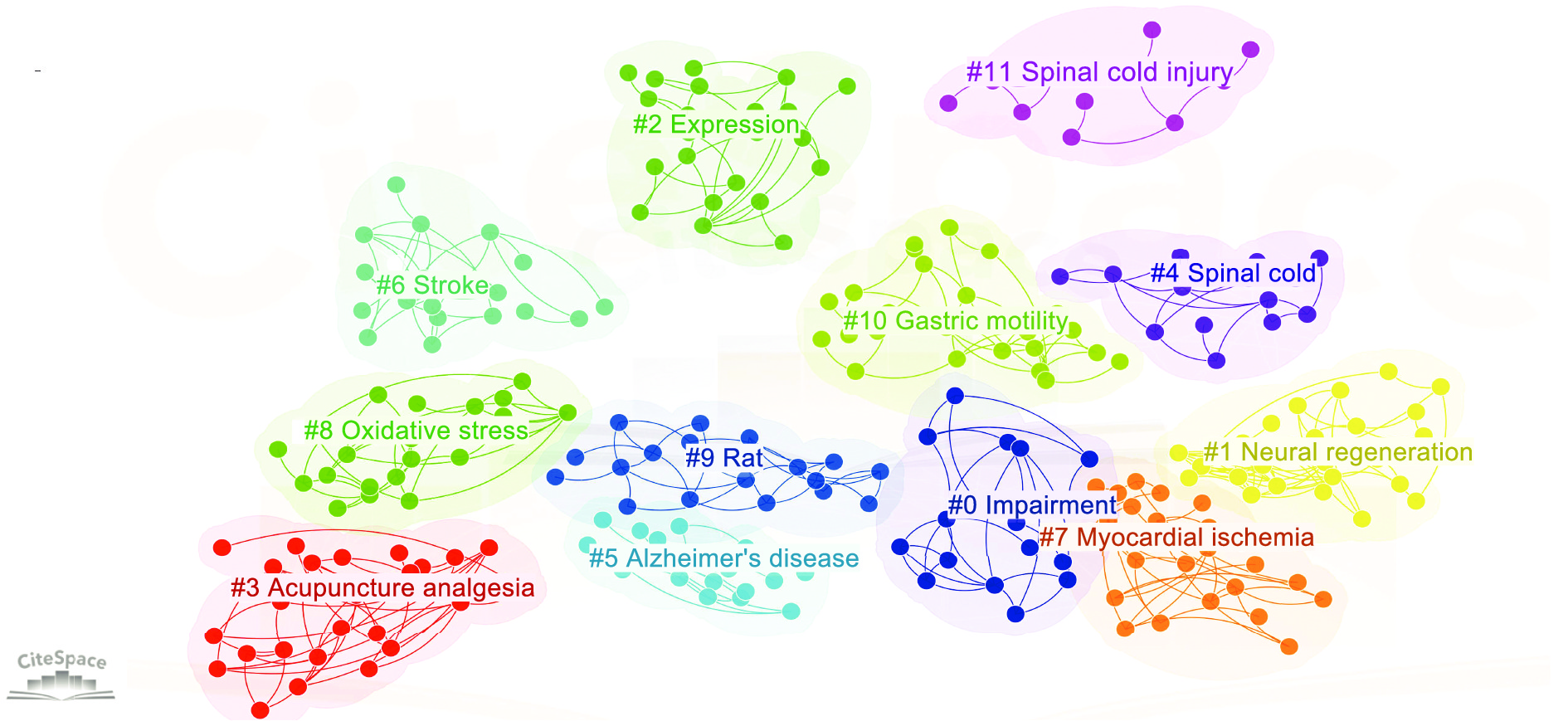
A total of 1 215 articles in the field of experimental acupuncture research in China were retrieved in Web of Science. CiteSpace was introduced to select the keyword latent semantic indexing (LSI) cluster. Further, the results were extracted from the literature keywords, and each cluster was automatically identified. There are 12 clusters, as shown in Table 8 and Figure 6, namely, impairment, neural regeneration, expression, acupuncture analgesia, spinal cord, Alzheimer's disease, stroke, myocardial ischaemia, oxidative stress, rat, gastric motility, and spinal cord injury. The mechanism of acupuncture on nerve regeneration or nerve recovery is an important topic in the research field, and many scholars have established mouse models of spinal cord injury, and conducted randomized controlled trials to explore the mechanism of acupuncture on nerve function recovery at the molecular level from different perspectives [23, 24]. The mechanism by which acupuncture improves Alzheimer's disease has been another key topic in recent years, and studies have found that acupuncture can improve cognitive status in Alzheimer's disease [25], but the mechanism remains unclear. Therefore, this topic has also been the focus of scholars' attention.
| Cluster ID | Size | Year | Terms (LSI) |
| 0 | 27 | 2013 | Acupuncture; analgesia; stimulation; involvement; mechanical allodynia; mechanism; impairment; electrical stimulation; myoelectrical activity; improves dyspeptic symptom |
| 1 | 23 | 2013 | Neural regeneration; nerve regeneration; traditional Chinese medicine; dorsal cord; upper cervical cord; grants-supported paper; irritable bowel syndrome; peripheral nerve injury; visceral hypersensitivity; photographs-containing paper |
| 2 | 22 | 2013 | Activation; acupuncture; mechanism; neuropathic pain; contribute; expression; pathway; protein degradation; atrophy; proteolysis |
| 3 | 22 | 2014 | Stimulation; electroacupuncture; pain; efficacy; preventing nausea; acupuncture; cerebral ischemia; moxibustion; acupoint; hippocampal |
| 4 | 21 | 2015 | Spinal cord; neuropathic pain; P2X4 receptor; chronic visceral hyperalgesia; Sanhuangshuai Decoction; mechanism; expression; activation; guideline; hyperalgesia |
| 5 | 20 | 2015 | Alzheimer’s disease; adenosine monophosphate-activated kinase; vascular dementia; Crohn’s disease; thioredoxin-interacting protein; brain; acupuncture; seizure; intractable epilepsy; rat model |
| 6 | 20 | 2013 | Acupuncture; receptor; electroacupuncture; in vivo; nerve stimulation; stroke; differentiation; expression; focal cerebral ischemia; proliferation |
| 7 | 19 | 2013 | Neuropathic pain; involvement; acupuncture; inflammatory pain; analgesia; cumulative effect; acupuncture analgesia; chronic neuropathic pain; memory impairment; cholinergic activities |
| 8 | 18 | 2012 | Oxidative stress; nucleus pulposus cell; intervertebral disc degeneration; cannabinoid type; exercise intensity; nerve regeneration; neural regeneration; ludmila belayev test; acupuncture treatment; tunel assay |
| 9 | 17 | 2014 | Electroacupuncture; pain; efficacy; sevoflurane; droperidol; acupuncture; stimulation; expression; inhibition; distension |
| 10 | 16 | 2014 | Acupuncture; inhibition; gastric motility; heterotopic acupoint; efficacy; electroacupuncture; protect; activation; ferroptosis; mediated autophagy |
| 11 | 12 | 2015 | Spinal cord injury; inflammatory response; erythroid 2-related factor; oxidative stress; nuclear factor; pathway; rat model; mouse; cyclase; hippocampus |
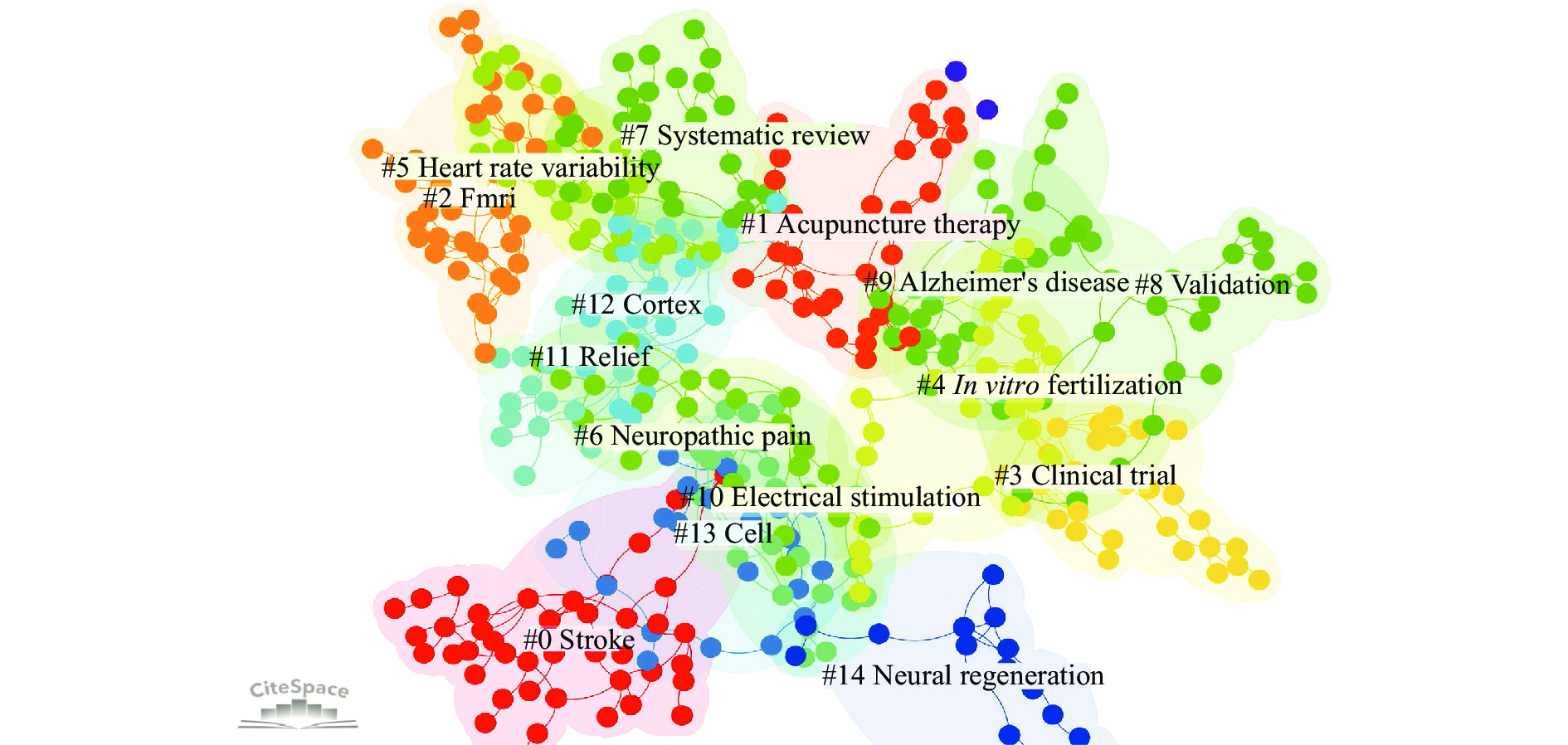
There are 3 805 articles of clinical acupuncture research in China in the recent decade. The keyword clustering yielded Figure 7 and Table 9, with the 15 clusters in the chart as follows: stroke, acupuncture therapy, frmi, clinical trial, in vitro fertilization, heart rate variability, neuropathic pain, systematic review, validation, Alzheimer's disease, electrical stimulation, relief, cortex, cell, and neural regeneration. Acupuncture for neuropathic pain, a common symptom, is a research topic. Several retrospective studies have shown that acupuncture plays a role in relieving pain associated with such lesions of the somatosensory system [26–28], but the quantity and quality of evidence are insufficient and further research is warranted. Acupuncture for dysfunctional disorders is a hot topic in this area of research, with studies demonstrating its efficacy in improving functional dyspepsia [29], cognitive disorders [30], and infertility [31].
| Cluster ID | Size | Year | Terms (LSI) |
| 0 | 43 | 2016 | Systematic review; transcutaneous electrical acupoint stimulation; cognitive function; postoperative cognitive dysfunction; maintenance disorders; controlled trial; recovery; pain; clinical trial; surgery |
| 1 | 36 | 2016 | Systematic review; auricular acupuncture; cancer-related depression; electrical acupuncture; general anesthesia; acupuncture therapy; controlled trials; maintenance disorders; sleep initiation; electrical acupuncture |
| 2 | 36 | 2015 | Stimulation; electroacupuncture; pain; efficacy; preventing nausea; functional magnetic resonance imaging; systems biology; Chinese herbal medicine; gastrointestinal disorder; Huiyang Shengji Formula |
| 3 | 30 | 2015 | Clinical trial; sensorineural tinnitus; pre-frontal cortex; Chinese herbal medicine; brain function; controlled trial; pre-frontal cortex; Chinese herbal medicine; Brain function; spinal column |
| 4 | 30 | 2015 | Systematic review; female infertility; risk assessment; subacute pain; sex hormone level; vitro fertilization; embryo transfer; clinical pregnancy rate; physiological rats; pituitary-ovary axis |
| 5 | 28 | 2016 | Functional dyspepsia; irritable bowel syndrome; functional constipation; functional gastrointestinal disorders; point; Parkinson's disease; iron accumulation; chronic visceral hyperalgesia; sham acupuncture; coronary artery disease |
| 6 | 28 | 2015 | Acupuncture; fatigue; quality; acupressure; insomnia; neuropathic pain; spinal cord; airway inflammation; risk assessment; interacting protein kinase |
| 7 | 27 | 2016 | Systematic review; risk assessment; posterior circulation ischemia; of-flight mass spectrometry; Chinese herbal medicine; polycystic ovary syndrome; insulin resistance; insulin sensitivity; sham acupuncture; homeostasis model assessment |
| 8 | 27 | 2014 | Controlled trial; acupuncture; involvement; adjunctive therapy; model; efficacy; electroacupuncture; stimulation; pain; preventing nausea |
| 9 | 26 | 2015 | Alzheimer’s disease; adenosine monophosphate-activated kinase; memory; network meta-analysis; multiple interventions; vascular dementia; cognitive impairment; expert consensus; breast cancer; pituitary gland |
| 10 | 26 | 2015 | Acupuncture; stroke; treatment; meta-analysis; insomnia; acupoint; nausea; relaxation; risk; acupressure |
| 11 | 25 | 2015 | Systematic review; phantom limb syndrome; phantom limb sensation; transcutaneous electric nerve stimulation; phantom limb pain; acupuncture; exercise; metaanalysis; pain; mobility |
| 12 | 23 | 2016 | Cortex; modulation; network; stimulation; therapy; complementary medicine; alternative medicine; functional connectivity; resting-state functional magnetic resonance; functional network |
| 13 | 23 | 2016 | Acupuncture; cell; histamine; transduction; lipid peroxidation; expression; pain; interleukin 1 production; st36; cyclooxygenase 2 |
| 14 | 23 | 2015 | Neural regeneration; nerve injury; cerebral palsy; botulinum toxin; constraint-induced movement therapy; nerve regeneration; selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor; primary unipolar depression; symptom checklist-90; signaling pathway |
A total of 551 pieces of literature abroad in the field of experimental acupuncture research were retrieved in Web of Science. There are 14 clusters, as shown in Figure 8 and Table 10, namely, neuron, bee venom, dexmedetomidine, visualization, traditional Chinese medicine, spinal cord, stimulation, antioxidant, long term potentiation, expression, apipuncture, Parkinson's disease, median nerve stimulation, and opioid receptors. Research on the mediators, receptors and signaling pathways involved in the anti-inflammatory and anti-nociceptive effects of acupuncture has been a central focus of experimental acupuncture research abroad. Goldman has reported that adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is released locally at acupuncture points in response to acupuncture stimulation to metabolize adenosine, activate adenosine A1 receptors, and produce analgesia in inflammatory pain [18]. A study by Torres Rosa demonstrated that there is in fact an anti-inflammatory pathway activated by electroacupuncture that involves the vagus and sciatic nerves, and is mediated by dopamine [32]. Meanwhile, global scholars have focused on the effects of electroacupuncture stimulation on the protective mechanisms of the cardiovascular system. YANG et al. [33] highlighted the neuroprotective effects of electroacupuncture on memory dysfunction, neuroinflammation, and glucose metabolism caused by bilateral common carotid artery occlusion, suggesting that electroacupuncture may be a treatment that can improve memory and reduce dementia-related neuroinflammation.
| Cluster ID | Size | Year | Terms (LSI) |
| 0 | 36 | 2015 | Trpa1 channel; blockade; ear acupuncture; cutaneous allodynia; gene related peptide; gaba; morphine; extinction; reinstatement; drug seeking |
| 1 | 32 | 2014 | Oxidative stress; propionic acid; neural cell death; comet assay; animal venom; Parkinson’s disease; motor dysfunction; amyotrophic lateral sclerosis; bee venom acupuncture; central nervous system |
| 2 | 26 | 2017 | Dexmedetomidine; acupuncture; analgesia; sedation; feline; impregnated polyethylene; benign esophageal; intestinal transit; acral lick dermatitis; fos protein |
| 3 | 22 | 2014 | Acupuncture; mammalian organ; surface; thread like structure; tissue; pain; release; microneedle; mechanism |
| 4 | 22 | 2014 | Electroacupuncture; expression; Parkinson’s disease; mechanism; neurogenesis; activation; acupuncture; inflammation; ganglion neuron; dorsal horn |
| 5 | 21 | 2014 | Spinal cord; seasonal allergic rhinitis; low frequency; involvement; inflammatory pain; dopamine d1; paraventricular nucleus; phospholipase c; ascending nociceptive control |
| 6 | 20 | 2015 | Acupuncture; stimulation; brain; thread like structure; surface; analgesia; neuropathic pain; morphine; questionnaire; pharmacokinetics |
| 7 | 20 | 2016 | Acupuncture; model; cell; classification; sclerosis; bee venom; dopamine; haloperidol; natural compounds; release |
| 8 | 20 | 2015 | Vascular dementia; dysfunction; Alzheimer’s disease; artery occlusion; brain-derived neurotrophic factor; camp-response element-binding protein; cholinergic neurons; chronic pain; cortical acetylcholine release |
| 9 | 19 | 2015 | Expression; edema; complementary; oncology; animal model;suppression; electroacupuncture; spinal glial activation; involvement; pain |
| 10 | 19 | 2014 | Acupuncture; acupoint stimulation; acupuncture point; nerve injury; model; water soluble fraction; neuropathic pain; modulation; activation; expression |
| 11 | 18 | 2014 | Parkinson's disease; motor dysfunction; resiniferatoxin; release; bone resorption; activation; macrophage infiltration; accumulation; insulin resistance; increase |
| 12 | 18 | 2014 | Parkinson's disease; motor function recovery; chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy; analgesia; atopic dermatitis; neuropathic pain; bee venom; motor function recovery; chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy; analgesia |
| 13 | 16 | 2014 | Blockade; acupuncture analgesia; dynorphin; endorphin; delta eeg; beta endorphin; chronic pain; mechanism; peptide; cord |
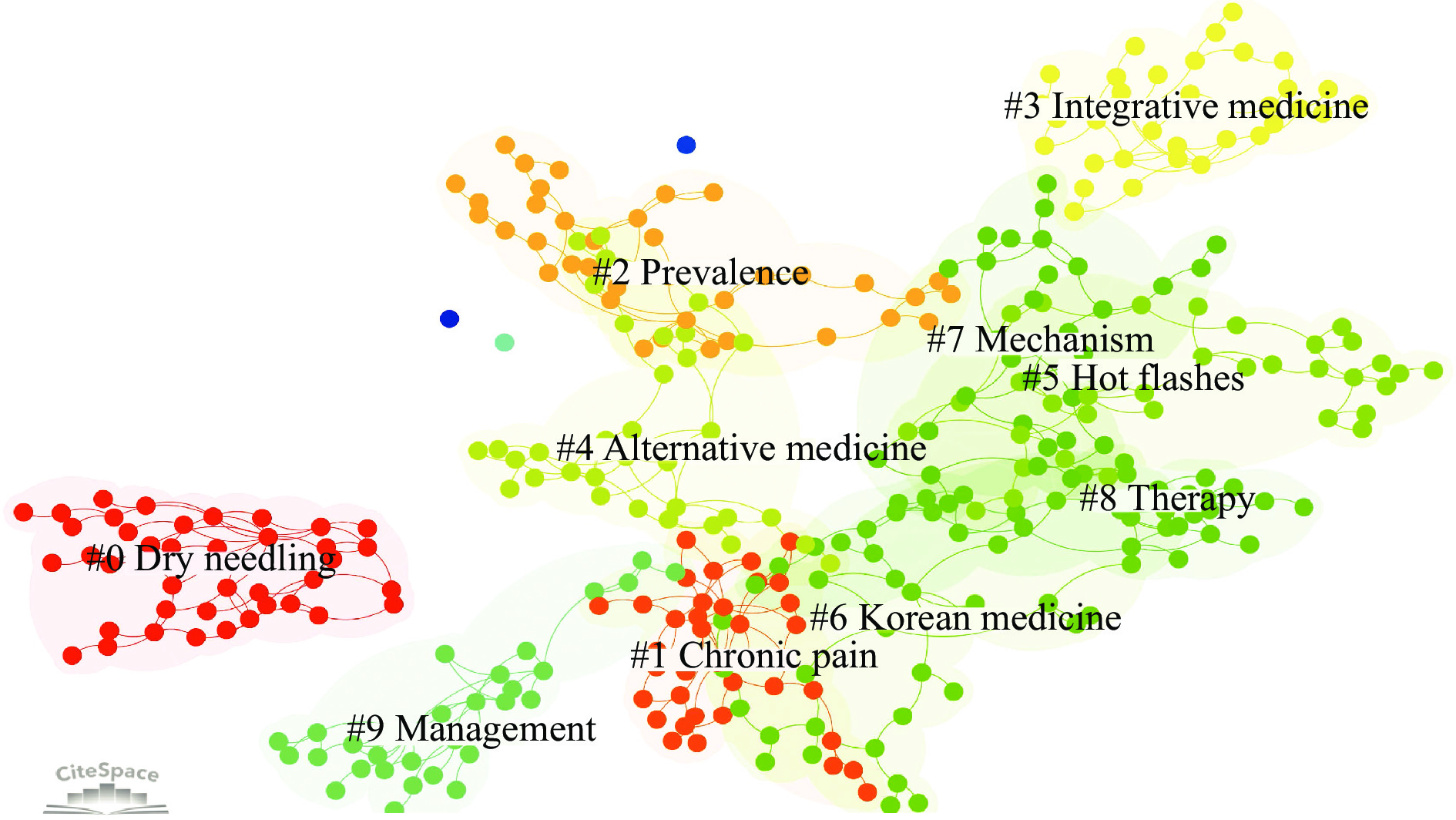
There are 4 538 articles of clinical acupuncture research abroad in recent 10 years, keywords were clustered, as shown in Figure 9 and Table 11. The 10 clusters were dry needling, chronic pain, prevalence, integrative medicine, alternative medicine, hot flashes, Korean medicine, mechanism, therapy, and management. The role of acupuncture in pain management has been an important topic, while foreign studies have focused more on the treatment of cancer [34], osteoarthritis of the knee [35], chronic pain [36], etc. In recent years, acupuncture for mood disorders such as depression and anxiety is also a key topic of acupuncture research abroad. A study by Peggy Bosch demonstrated that acupuncture is an effective and safe treatment for major depression, and that sleep and quality of life (involving mood) in patients with depression and schizophrenia can be improved with acupuncture treatment [37].
| Cluster ID | Size | Year | Terms (LSI) |
| 0 | 41 | 2014 | Dry needling; needle tenotomy; tendon fenestration; patient anxiety; chronic fatigue disorders; controlled trial; traffic accident; clinical trial protocol; pain; low-level laser |
| 1 | 38 | 2014 | Chronic pain; complementary therapies; health knowledge; health personnel; negative findings; stimulation; manual acupuncture; trigger point; blood flow; moxibustion |
| 2 | 37 | 2014 | Breast cancer; neck cancer; symptom burden; randomized controlled trial; chronic migraine; alternative medicine; traditional medicine; mind-body medicine; irritable bowel syndrome; education |
| 3 | 35 | 2015 | Alternative medicine; complementary therapies; longitudinal analyses; hysterectomy oophorectomy; systems biology; integrative medicine; mood disorders; systems biology; general practitioner; endocrine system |
| 4 | 35 | 2013 | Alternative medicine; herbal medicine; massage therapy; parent; disability index; complementary medicine; parent; disability index; knee osteoarthritis ; dysmenorrhea |
| 5 | 35 | 2015 | Hot flashes; androgen deprivation therapy; chemotherapy-induced nausea; home care device; high-intensity exercise; breast cancer; systematic review; chemotherapy-induced nausea; home care device; high-intensity exercise |
| 6 | 32 | 2014 | Alternative medicine; herbal medicine; massage therapy; knee osteoarthritis; home care device; systematic review; knee osteoarthritis; home care device; underserved area; chinese herbal medicine |
| 7 | 32 | 2014 | Acupuncture; mechanism; analgesia; zusanli acupoint; rat model; system; expression; activation; trpv1 channel; pathway |
| 8 | 31 | 2014 | Therapy; medicine; children; acupressure; auricular acupuncture; acupuncture; depression; qualitative; research; antenatal |
| 9 | 31 | 2014 | Acupuncture; therapy; placebo; symptom; multicenter; management; care; relief; preterm; familiar odor |
From the number of articles, it can be drawn that global acupuncture research has reached a stable period, and domestic acupuncture research is developing rapidly. In recent years, the annual publication volume in China has exceeded that abroad.
From the analysis of the authors, LIU Cunzhi from China and Lee Myeong Soo from South Korea made important contributions, and they also led the formation of their respective research cooperation networks. There are collaborative relationships among authors in different collaborative networks, but the intensity of collaboration is relatively low. The construction of the international cooperation network of authors in the field of acupuncture needs to be further strengthened. The same holds true for cooperation between countries.
In journal analyses, most of the journals with high publication volume are in the JCR Q3 and Q4, and most of them are English journals located in the USA. The construction of journals in the field of acupuncture needs to be reinforced urgently.
Through the analysis of keywords and references, we found that acupuncture analgesia is an important topic of common concern in China and abroad. In China, more emphasis is placed on the therapeutic effect of acupuncture on visceral pain, stroke, neuropathic pain, and other non-traumatic pain, while more emphasis is put on the role of acupuncture or electroacupuncture at the molecular or cellular level in anti-inflammatory and analgesic mechanisms abroad. As a traditional therapy, acupuncture has marked effects in treating various difficult and miscellaneous diseases. The application of acupuncture in China mainly centered on the treatment of internal medicine diseases, such as functional dyspepsia, endocrine disorders, and other diseases, while global studies are more focused on the treatment of cancer and mental diseases. It can be predicted that in the future, domestic acupuncture research may pay more attention to the treatment of internal diseases, such as visceral pain, spinal pain, visceral dysfunction, etc. Acupuncture treatment of inflammatory pain and psychological disorders is expected to become the future trend of acupuncture research abroad.
In summary, this study used the bibliometric method to sort out and analyze the current situation and hotspots of acupuncture research in China and abroad in the past decade, and predicted the future research directions in China and abroad. However, the present study also has objective limitations. On one hand, the data were only obtained from the acupuncture-related literature from the Web of Science database, so some articles published in other databases were not included in the analysis. On the other hand, due to the limitation of specific retrieval methods, some acupuncture articles may not be collected, and the overall study may have deviation.
In this study, bibliometrics was employed to conduct a comprehensive analysis of acupuncture research in China and abroad in the past decade. The results show that acupuncture research has established several stable cooperation teams, but the cooperation between the author's cooperation network and countries is not close. It is necessary to promote the standardization construction and international exchange of acupuncture, and strengthen the cooperation between institutions and countries. Acupuncture analgesia research is an eternal research focus in this field, but in clinical application, there are differences between Chinese and global research focus. In China, more attention is paid to the treatment of internal medicine diseases and pain, while in foreign countries, attention is attached to the alleviation and improvement of acupuncture on cancer and psychosocial diseases.
Scientific and Technological Innovation Project of China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences (CI2021B002 and CI2021A00501).
| [1] |
ALLEN J, MAK S, BEGASHAW M, et al. Use of acupuncture for adult health conditions, 2013 to 2021 a systematic review. JAMA Network Open, 2022, 5(11): e2243665. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.43665
|
| [2] |
KUNG YY, HWANG SJ, LI TF, et al. Trends in global acupuncture publications: an analysis of the Web of Science database from 1988 to 2015. Journal of the Chinese Medical Association, 2017, 80(8): 521–525. doi: 10.1016/j.jcma.2017.01.010
|
| [3] |
LEE IS, CHAE Y. A bibliometric analysis of acupuncture research trends in acupuncture in medicine. Acupuncture in Medicine, 2019, 37(6): 375–377. doi: 10.1177/0964528419884327
|
| [4] |
CHEN C, SONG M. Visualizing a field of research: A methodology of systematic scientometric reviews. PLoS One, 2019, 14(10): e0223994. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0223994
|
| [5] |
KIM TH, LEE MS, ALRAEK T, et al. Acupuncture in sham device controlled trials may not be as effective as acupuncture in the real world: a preliminary network meta-analysis of studies of acupuncture for hot flashes in menopausal women. Acupuncture in Medicine, 2020, 38(1): 37–44. doi: 10.1136/acupmed-2018-011671
|
| [6] |
KIM TH, LEE MS, BIRCH S, et al. Plausible mechanism of sham acupuncture based on biomarkers: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 2022, 16: 834112. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.834112
|
| [7] |
KIM D, CHAE Y, PARK H, et al. Effects of chronic pain treatment on altered functional and metabolic activities in the brain: a systematic review and meta-analysis of functional neuroimaging studies. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 2021, 15: 684926. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.684926
|
| [8] |
LEE H, ANG L, LEE M, et al. Prescription patterns of herbal medicine for polycystic ovarian syndrome in major Korean medicine hospitals: a multicenter retrospective study. Clinical and Experimental Obstetrics & Gynecology, 2021, 48(3): 649–653.
|
| [9] |
YU SY, XIE MG, LIU SQ, et al. Resting-state functional connectivity patterns predict acupuncture treatment response in primary dysmenorrhea. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 2020, 14: 559191. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2020.559191
|
| [10] |
WANG YA, XU J, ZHANG Q, et al. Immediate analgesic effect of acupuncture in patients with primary dysmenorrhea: a fMRI study. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 2021, 15: 647667. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.647667
|
| [11] |
SU C, HAN P, JIANG B, et al. A TCM acupoints ranking approach towards post-stroke dysphagia based on an improved MCTS decision method. Technology and Health Care, 2019, 27: 367–381. doi: 10.3233/THC-199034
|
| [12] |
FEI XX, ZENG Q, WANG JX, et al. Bibliometric analysis of 100 most-cited articles in delirium. Frontiers in Psychiatry, 2022, 13: 931632. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2022.931632
|
| [13] |
HAN JS. Acupuncture: neuropeptide release produced by electrical stimulation of different frequencies. Trends in Neurosciences, 2003, 26(1): 17–22. doi: 10.1016/S0166-2236(02)00006-1
|
| [14] |
KAPTCHUK TJ. Acupuncture: theory, efficacy, and practice. Annals of Internal Medicine, 2002, 136(5): 374–383. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-136-5-200203050-00010
|
| [15] |
MOHER D, LIBERATI A, TETZLAFF J, et al. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. Physical Therapy, 2009, 89(9): 873–880. doi: 10.1093/ptj/89.9.873
|
| [16] |
GUYATT GH, OXMAN AD, VIST GE, et al. GRADE: an emerging consensus on rating quality of evidence and strength of recommendations. British Medical Journal, 2008, 336(7650): 924–926. doi: 10.1136/bmj.39489.470347.AD
|
| [17] |
HIGGINS JP, THOMPSON SG, DEEKS JJ, et al. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. British Medical Journal, 2003, 327(7414): 557–560. doi: 10.1136/bmj.327.7414.557
|
| [18] |
GOLDMAN N, CHEN M, FUJITA T, et al. Adenosine A1 receptors mediate local anti-nociceptive effects of acupuncture. Nature Neuroscience, 2010, 13(7): 883–888. doi: 10.1038/nn.2562
|
| [19] |
HAN JS. Acupuncture and endorphins. Neuroscience Letters, 2004, 361(1-3): 258–261. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2003.12.019
|
| [20] |
VICKERS AJ, CRONIN AM, MASCHINO AC, et al. Acupuncture for chronic pain individual patient data meta-analysis. Archives of Internal Medicine, 2012, 172(19): 1444–1453. doi: 10.1001/archinternmed.2012.3654
|
| [21] |
EISENBERG DM, DAVIS RB, ETTNER SL, et al. Trends in alternative medicine use in the United States, 1990-1997: results of a follow-up national survey. JAMA, 1998, 280(18): 1569–1575. doi: 10.1001/jama.280.18.1569
|
| [22] |
ELLEGAARD O, WALLIN JA. The bibliometric analysis of scholarly production: how great is the impact? Scientometrics, 2015, 105(3): 1809–1831.
|
| [23] |
YANG JH, LV JG, WANG H, et al. Electroacupuncture promotes the recovery of motor neuron function in the anterior horn of the injured spinal cord. Neural Regeneration Research, 2015, 10(12): 2033–2039. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.172323
|
| [24] |
TANG HL, GUO Y, ZHAO YD, et al. Effects and mechanisms of acupuncture combined with mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on neural recovery after spinal cord injury: progress and prospects. Neural Plasticity, 2020, 2020: 8890655.
|
| [25] |
KAN BH, YU JC, ZHAO L, et al. Acupuncture improves dendritic structure and spatial learning and memory ability of Alzheimer’s disease mice. Neural Regeneration Research, 2018, 13(8): 1390–1395. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.235292
|
| [26] |
HE KL, HU R, HUANG Y, et al. Effects of acupuncture on neuropathic pain induced by spinal cord injury: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine, 2022, 2022: 6297484.
|
| [27] |
JU ZY, WANG K, CUI HS, et al. Acupuncture for neuropathic pain in adults. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, 2017, (12): CD012057.
|
| [28] |
WANG LQ, GAO ZH, NIU XR, et al. Acupuncture for diabetic neuropathic pain: a protocol for systematic review and meta analysis. Medicine, 2020, 99(47): e23244. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000023244
|
| [29] |
ZHANG JH, LIU YF, HUANG XX, et al. Efficacy comparison of different acupuncture treatments for functional dyspepsia: a systematic review with network meta-analysis. Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine, 2020, 2020: 3872919.
|
| [30] |
LI RY, HUANG RJ, YU Q. Comparison of different physical therapies combined with acupuncture for poststroke cognitive impairment: a network meta-analysis. Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine, 2021, 2021: 1101101.
|
| [31] |
WU J, NING Y, YE Y, et al. Effects of acupuncture on endometrium and pregnancy outcomes in patients with polycystic ovarian syndrome undergoing in vitro fertilization-embryo transfer: a randomized clinical trial. Chinese Journal of Integrative Medicine, 2022, 28(8): 736–742. doi: 10.1007/s11655-022-3498-z
|
| [32] |
TORRES RR, YEHIA G, PENA G, et al. Dopamine mediates vagal modulation of the immune system by electroacupuncture. Nature Medicine, 2014, 20(3): 291–295. doi: 10.1038/nm.3479
|
| [33] |
YANG EJ, CAI M, LEE JH. Neuroprotective effects of electroacupuncture on an animal model of bilateral common carotid artery occlusion. Molecular Neurobiology, 2016, 53(10): 7228–7236. doi: 10.1007/s12035-015-9610-7
|
| [34] |
BIRCH S, LEE MS, ALRAEK T, et al. Evidence, safety and recommendations for when to use acupuncture for treating cancer related symptoms: a narrative review. Integrative Medicine Research, 2019, 8(3): 160–166. doi: 10.1016/j.imr.2019.05.002
|
| [35] |
JUN P, HAN C, YANG C, et al. Efficacy and safety of thread embedding acupuncture on knee osteoarthritis: a randomized, controlled, pilot clinical trial. Medicine, 2020, 99(36): e21957. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000021957
|
| [36] |
MOURA C, CHAVES E, CHIANCA T, et al. Contribution of Chinese and French ear acupuncture for the management of chronic back pain: a randomised controlled trial. Journal of Clinical Nursing, 2019, 28(21-22): 3796–3806. doi: 10.1111/jocn.14983
|
| [37] |
BOSCH P, VANDEN NM, STAUDTE H, et al. Schizophrenia and depression: a systematic review of the effectiveness and the working mechanisms behind acupuncture. Explore: The Journal of Science and Healing, 2015, 11(4): 281–291.
|
| No. | Author | Institution | Country | n (%) |
| 1 | LIU Cunzhi | Beijing Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine | China | 90 (0.98%) |
| 2 | Lee Myeong Soo | Korea Institute of Oriental Medicine | South Korea | 89 (0.97%) |
| 3 | LIU Zhishun | China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences | China | 80 (0.87%) |
| 4 | LAO Lixing | University of Hong Kong | China | 75 (0.82%) |
| 5 | LIANG Fanrong | Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine | China | 68 (0.74%) |
| 6 | Park Hi Joon | Kyung Hee University | South Korea | 61 (0.67%) |
| 7 | LI Ying | Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine | China | 59 (0.64%) |
| 8 | YANG Jingwen | Hefei University of Technology | China | 57 (0.62%) |
| 9 | SHI Guangxia | Beijing University of Chinese Medicine | China | 50 (0.55%) |
| 10 | ZHAO Ling | Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine | China | 49 (0.54%) |
| No. | Country | n (%) |
| 1 | China | 4 844 (52.91%) |
| 2 | USA | 1 710 (18.68%) |
| 3 | South Korea | 964 (10.53%) |
| 4 | England | 472 (5.16%) |
| 5 | Australia | 417 (4.55%) |
| 6 | Germany | 313 (3.42%) |
| 7 | Brazil | 269 (2.94%) |
| 8 | Canada | 256 (2.80%) |
| 9 | Japan | 178 (1.94%) |
| 10 | Italy | 161 (1.76%) |
| No. | Journal | IF-2021/JCR | Country | n |
| 1 | Evidence-based Complementary and Alternative Medicine | 2.650/Q3 | England | 958 |
| 2 | Medicine | 1.817/Q3 | US | 674 |
| 3 | Acupuncture in Medicine | 1.976/Q3 | UK | 498 |
| 4 | Trials | 2.728/Q4 | US | 284 |
| 5 | Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine | 2.381/Q3 | US | 256 |
| 6 | BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine | 4.782/Q1 | UK | 224 |
| 7 | European Journal of Integrative Medicine | 1.813/Q4 | Germany | 169 |
| 8 | Complementary Therapies in Medicine | 3.335/Q2 | UK | 166 |
| 9 | Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine | 2.547/Q3 | China | 166 |
| 10 | PLoS One | 3.752/Q2 | US | 160 |
| No. | Title | Journal | IF-2021/JCR | Total cites | Year |
| 1 | Acupuncture: neuropeptide release produced by electrical stimulation of different frequencies | Trends in Neurosciences | 16.978/Q1 | 79 | 2003 |
| 2 | Adenosine A1 receptors mediate local anti-nociceptive effects of acupuncture | Nature Neuroscience | 28.771/Q1 | 70 | 2010 |
| 3 | Acupuncture and endorphins | Neuroscience Letters | 3.197/Q3 | 34 | 2004 |
| 4 | Quantitative assessment of tactile allodynia in the rat paw | Journal of Neuroscience Methods | 2.987/Q3 | 32 | 1994 |
| 5 | Acupuncture: theory, efficacy, and practice | Annals of Internal Medicine | 51.598/Q1 | 28 | 2002 |
| 6 | A new model of chronic visceral hypersensitivity in adult rats induced by colon irritation during postnatal development | Gastroenterology | 33.883/Q1 | 26 | 2000 |
| 7 | A peripheral mononeuropathy in rat that produces disorders of pain sensation like those seen in man | Pain | 7.926/Q1 | 25 | 1988 |
| 8 | Acupuncture analgesia: areas of consensus and controversy | Pain | 7.926/Q1 | 24 | 2011 |
| 9 | Acupuncture: a novel hypothesis for the involvement of purinergic signalling | Medical Hypotheses | 4.411/Q2 | 22 | 2009 |
| 10 | Electroacupuncture exerts anti-inflammatory effects in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injured rats via suppression of the TLR4/NF-κB pathway | International Journal of Molecular Medicine | 5.314/Q2 | 21 | 2013 |
| No. | Title | Journal | IF-2021/JCR | Total cites | Year |
| 1 | Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015 statement | BMJ | 93.333/Q1 | 145 | 2009 |
| 2 | Cognitive-behavioural interventions for children who have been sexually abused (Review) | Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews | 12.008/Q1 | 116 | 2012 |
| 3 | Acupuncture: neuropeptide release produced by electrical stimulation of different frequencies | Trends in Neurosciences | 16.978/Q1 | 115 | 2003 |
| 4 | Acupuncture: theory, efficacy, and practice | Annals of Internal Medicine | 51.598/Q1 | 110 | 2002 |
| 5 | Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement | BMJ | 93.333/Q1 | 109 | 2009 |
| 6 | Neural mechanism underlying acupuncture analgesia | Progress in Neurobiology | 10.885/Q1 | 109 | 2008 |
| 7 | GRADE: an emerging consensus on rating quality of evidence and strength of recommendations | BMJ | 93.333/Q1 | 106 | 2008 |
| 8 | Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses | BMJ | 93.333/Q1 | 104 | 2003 |
| 9 | Acupuncture for chronic pain individual patient data meta-analysis | JAMA Internal Medicine | 44.409/Q1 | 104 | 2012 |
| 10 | Revised standards for reporting interventions in clinical trials of acupuncture (STRICTA): extending the CONSORT statement | PLoS Medicine | 11.613/Q1 | 103 | 2010 |
| No. | Title | Journal | IF-2021/JCR | Total cites | Year |
| 1 | Adenosine A1 receptors mediate local anti-nociceptive effects of acupuncture | Nature Neuroscience | 28.771/Q1 | 63 | 2010 |
| 2 | Neural mechanism underlying acupuncture analgesia | Progress in Neurobiology | 10.885/Q1 | 56 | 2008 |
| 3 | Acupuncture: neuropeptide release produced by electrical stimulation of different frequencies | Trends in Neurosciences | 16.978/Q1 | 48 | 2003 |
| 4 | A proposed transpositional acupoint system in a mouse and rat model | Research in Veterinary Science | 2.554/Q1 | 48 | 2008 |
| 5 | Ethical Guidelines for investigations of Experimental Pain in Conscious Animals | Pain | 7.926/Q1 | 30 | 1983 |
| 6 | Acupuncture and endorphins | Neuroscience Letters | 3.197/Q3 | 28 | 2004 |
| 7 | Mechanisms of acupuncture-electroacupuncture on persistent pain | Anesthesiology | 8.986/Q1 | 27 | 2014 |
| 8 | Mechanical signaling through connective tissue: a mechanism for the therapeutic effect of acupuncture | Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology Journal | 5.834/Q1 | 23 | 2001 |
| 9 | Therapeutic application of anti-arthritis, pain-releasing, and anti-cancer effects of bee venom and its constituent compounds | Pharmacol Therapeut | 13.400/Q1 | 23 | 2007 |
| 10 | The central serotonergic system mediates the analgesic effect of electroacupuncture on Zusanli (ST36) acupoints | Journal of Biomedical Science | 12.771/Q1 | 22 | 2004 |
| No. | Title | Journal | IF-2021/JCR | Total cites | Year |
| 1 | Acupuncture for chronic pain individual patient data meta-analysis | Archives of Internal Medicine | 44.409/Q1 | 254 | 2012 |
| 2 | Neural mechanism underlying acupuncture analgesia | Progress in Neurobiology | 10.885/Q1 | 157 | 2008 |
| 3 | Acupuncture and endorphins | Neuroscience Letters | 3.197/Q3 | 112 | 2004 |
| 4 | German acupuncture trials (GERAC) for chronic low back pain | Archives of Internal Medicine | 44.409/Q1 | 106 | 2007 |
| 5 | Introducing a placebo needle into acupuncture research | The Lancet | 202.731/Q1 | 104 | 1998 |
| 6 | Safety of acupuncture: results of a prospective observational study with 229 230 patients and introduction of a medical information and consent form | Forschende Komplementarmedizin | 1.306/Q4 | 98 | 2009 |
| 7 | Acupuncture: theory, efficacy, and practice | Annals of Internal Medicine | 51.598/Q1 | 94 | 2002 |
| 8 | Trends in alternative medicine use in the United States, 1990 -1997 results of a follow-up national survey | JAMA | 157.335/Q1 | 93 | 1998 |
| 9 | The impact of patient expectations on outcomes in four randomized controlled trials of acupuncture in patients with chronic pain | Pain | 7.926/Q1 | 93 | 2007 |
| 10 | Adenosine A1 receptors mediate local anti-nociceptive effects of acupuncture | Nature Neuroscience | 28.771/Q1 | 91 | 2010 |
| Cluster ID | Size | Year | Terms (LSI) |
| 0 | 27 | 2013 | Acupuncture; analgesia; stimulation; involvement; mechanical allodynia; mechanism; impairment; electrical stimulation; myoelectrical activity; improves dyspeptic symptom |
| 1 | 23 | 2013 | Neural regeneration; nerve regeneration; traditional Chinese medicine; dorsal cord; upper cervical cord; grants-supported paper; irritable bowel syndrome; peripheral nerve injury; visceral hypersensitivity; photographs-containing paper |
| 2 | 22 | 2013 | Activation; acupuncture; mechanism; neuropathic pain; contribute; expression; pathway; protein degradation; atrophy; proteolysis |
| 3 | 22 | 2014 | Stimulation; electroacupuncture; pain; efficacy; preventing nausea; acupuncture; cerebral ischemia; moxibustion; acupoint; hippocampal |
| 4 | 21 | 2015 | Spinal cord; neuropathic pain; P2X4 receptor; chronic visceral hyperalgesia; Sanhuangshuai Decoction; mechanism; expression; activation; guideline; hyperalgesia |
| 5 | 20 | 2015 | Alzheimer’s disease; adenosine monophosphate-activated kinase; vascular dementia; Crohn’s disease; thioredoxin-interacting protein; brain; acupuncture; seizure; intractable epilepsy; rat model |
| 6 | 20 | 2013 | Acupuncture; receptor; electroacupuncture; in vivo; nerve stimulation; stroke; differentiation; expression; focal cerebral ischemia; proliferation |
| 7 | 19 | 2013 | Neuropathic pain; involvement; acupuncture; inflammatory pain; analgesia; cumulative effect; acupuncture analgesia; chronic neuropathic pain; memory impairment; cholinergic activities |
| 8 | 18 | 2012 | Oxidative stress; nucleus pulposus cell; intervertebral disc degeneration; cannabinoid type; exercise intensity; nerve regeneration; neural regeneration; ludmila belayev test; acupuncture treatment; tunel assay |
| 9 | 17 | 2014 | Electroacupuncture; pain; efficacy; sevoflurane; droperidol; acupuncture; stimulation; expression; inhibition; distension |
| 10 | 16 | 2014 | Acupuncture; inhibition; gastric motility; heterotopic acupoint; efficacy; electroacupuncture; protect; activation; ferroptosis; mediated autophagy |
| 11 | 12 | 2015 | Spinal cord injury; inflammatory response; erythroid 2-related factor; oxidative stress; nuclear factor; pathway; rat model; mouse; cyclase; hippocampus |
| Cluster ID | Size | Year | Terms (LSI) |
| 0 | 43 | 2016 | Systematic review; transcutaneous electrical acupoint stimulation; cognitive function; postoperative cognitive dysfunction; maintenance disorders; controlled trial; recovery; pain; clinical trial; surgery |
| 1 | 36 | 2016 | Systematic review; auricular acupuncture; cancer-related depression; electrical acupuncture; general anesthesia; acupuncture therapy; controlled trials; maintenance disorders; sleep initiation; electrical acupuncture |
| 2 | 36 | 2015 | Stimulation; electroacupuncture; pain; efficacy; preventing nausea; functional magnetic resonance imaging; systems biology; Chinese herbal medicine; gastrointestinal disorder; Huiyang Shengji Formula |
| 3 | 30 | 2015 | Clinical trial; sensorineural tinnitus; pre-frontal cortex; Chinese herbal medicine; brain function; controlled trial; pre-frontal cortex; Chinese herbal medicine; Brain function; spinal column |
| 4 | 30 | 2015 | Systematic review; female infertility; risk assessment; subacute pain; sex hormone level; vitro fertilization; embryo transfer; clinical pregnancy rate; physiological rats; pituitary-ovary axis |
| 5 | 28 | 2016 | Functional dyspepsia; irritable bowel syndrome; functional constipation; functional gastrointestinal disorders; point; Parkinson's disease; iron accumulation; chronic visceral hyperalgesia; sham acupuncture; coronary artery disease |
| 6 | 28 | 2015 | Acupuncture; fatigue; quality; acupressure; insomnia; neuropathic pain; spinal cord; airway inflammation; risk assessment; interacting protein kinase |
| 7 | 27 | 2016 | Systematic review; risk assessment; posterior circulation ischemia; of-flight mass spectrometry; Chinese herbal medicine; polycystic ovary syndrome; insulin resistance; insulin sensitivity; sham acupuncture; homeostasis model assessment |
| 8 | 27 | 2014 | Controlled trial; acupuncture; involvement; adjunctive therapy; model; efficacy; electroacupuncture; stimulation; pain; preventing nausea |
| 9 | 26 | 2015 | Alzheimer’s disease; adenosine monophosphate-activated kinase; memory; network meta-analysis; multiple interventions; vascular dementia; cognitive impairment; expert consensus; breast cancer; pituitary gland |
| 10 | 26 | 2015 | Acupuncture; stroke; treatment; meta-analysis; insomnia; acupoint; nausea; relaxation; risk; acupressure |
| 11 | 25 | 2015 | Systematic review; phantom limb syndrome; phantom limb sensation; transcutaneous electric nerve stimulation; phantom limb pain; acupuncture; exercise; metaanalysis; pain; mobility |
| 12 | 23 | 2016 | Cortex; modulation; network; stimulation; therapy; complementary medicine; alternative medicine; functional connectivity; resting-state functional magnetic resonance; functional network |
| 13 | 23 | 2016 | Acupuncture; cell; histamine; transduction; lipid peroxidation; expression; pain; interleukin 1 production; st36; cyclooxygenase 2 |
| 14 | 23 | 2015 | Neural regeneration; nerve injury; cerebral palsy; botulinum toxin; constraint-induced movement therapy; nerve regeneration; selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor; primary unipolar depression; symptom checklist-90; signaling pathway |
| Cluster ID | Size | Year | Terms (LSI) |
| 0 | 36 | 2015 | Trpa1 channel; blockade; ear acupuncture; cutaneous allodynia; gene related peptide; gaba; morphine; extinction; reinstatement; drug seeking |
| 1 | 32 | 2014 | Oxidative stress; propionic acid; neural cell death; comet assay; animal venom; Parkinson’s disease; motor dysfunction; amyotrophic lateral sclerosis; bee venom acupuncture; central nervous system |
| 2 | 26 | 2017 | Dexmedetomidine; acupuncture; analgesia; sedation; feline; impregnated polyethylene; benign esophageal; intestinal transit; acral lick dermatitis; fos protein |
| 3 | 22 | 2014 | Acupuncture; mammalian organ; surface; thread like structure; tissue; pain; release; microneedle; mechanism |
| 4 | 22 | 2014 | Electroacupuncture; expression; Parkinson’s disease; mechanism; neurogenesis; activation; acupuncture; inflammation; ganglion neuron; dorsal horn |
| 5 | 21 | 2014 | Spinal cord; seasonal allergic rhinitis; low frequency; involvement; inflammatory pain; dopamine d1; paraventricular nucleus; phospholipase c; ascending nociceptive control |
| 6 | 20 | 2015 | Acupuncture; stimulation; brain; thread like structure; surface; analgesia; neuropathic pain; morphine; questionnaire; pharmacokinetics |
| 7 | 20 | 2016 | Acupuncture; model; cell; classification; sclerosis; bee venom; dopamine; haloperidol; natural compounds; release |
| 8 | 20 | 2015 | Vascular dementia; dysfunction; Alzheimer’s disease; artery occlusion; brain-derived neurotrophic factor; camp-response element-binding protein; cholinergic neurons; chronic pain; cortical acetylcholine release |
| 9 | 19 | 2015 | Expression; edema; complementary; oncology; animal model;suppression; electroacupuncture; spinal glial activation; involvement; pain |
| 10 | 19 | 2014 | Acupuncture; acupoint stimulation; acupuncture point; nerve injury; model; water soluble fraction; neuropathic pain; modulation; activation; expression |
| 11 | 18 | 2014 | Parkinson's disease; motor dysfunction; resiniferatoxin; release; bone resorption; activation; macrophage infiltration; accumulation; insulin resistance; increase |
| 12 | 18 | 2014 | Parkinson's disease; motor function recovery; chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy; analgesia; atopic dermatitis; neuropathic pain; bee venom; motor function recovery; chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy; analgesia |
| 13 | 16 | 2014 | Blockade; acupuncture analgesia; dynorphin; endorphin; delta eeg; beta endorphin; chronic pain; mechanism; peptide; cord |
| Cluster ID | Size | Year | Terms (LSI) |
| 0 | 41 | 2014 | Dry needling; needle tenotomy; tendon fenestration; patient anxiety; chronic fatigue disorders; controlled trial; traffic accident; clinical trial protocol; pain; low-level laser |
| 1 | 38 | 2014 | Chronic pain; complementary therapies; health knowledge; health personnel; negative findings; stimulation; manual acupuncture; trigger point; blood flow; moxibustion |
| 2 | 37 | 2014 | Breast cancer; neck cancer; symptom burden; randomized controlled trial; chronic migraine; alternative medicine; traditional medicine; mind-body medicine; irritable bowel syndrome; education |
| 3 | 35 | 2015 | Alternative medicine; complementary therapies; longitudinal analyses; hysterectomy oophorectomy; systems biology; integrative medicine; mood disorders; systems biology; general practitioner; endocrine system |
| 4 | 35 | 2013 | Alternative medicine; herbal medicine; massage therapy; parent; disability index; complementary medicine; parent; disability index; knee osteoarthritis ; dysmenorrhea |
| 5 | 35 | 2015 | Hot flashes; androgen deprivation therapy; chemotherapy-induced nausea; home care device; high-intensity exercise; breast cancer; systematic review; chemotherapy-induced nausea; home care device; high-intensity exercise |
| 6 | 32 | 2014 | Alternative medicine; herbal medicine; massage therapy; knee osteoarthritis; home care device; systematic review; knee osteoarthritis; home care device; underserved area; chinese herbal medicine |
| 7 | 32 | 2014 | Acupuncture; mechanism; analgesia; zusanli acupoint; rat model; system; expression; activation; trpv1 channel; pathway |
| 8 | 31 | 2014 | Therapy; medicine; children; acupressure; auricular acupuncture; acupuncture; depression; qualitative; research; antenatal |
| 9 | 31 | 2014 | Acupuncture; therapy; placebo; symptom; multicenter; management; care; relief; preterm; familiar odor |